
2 Billion Tonnes
of municipal solid waste is produced per year globally, and is expected to nearly double by 2050.

23%
of global methane emissions are generated by landfilling of organic waste, despite capture technologies.
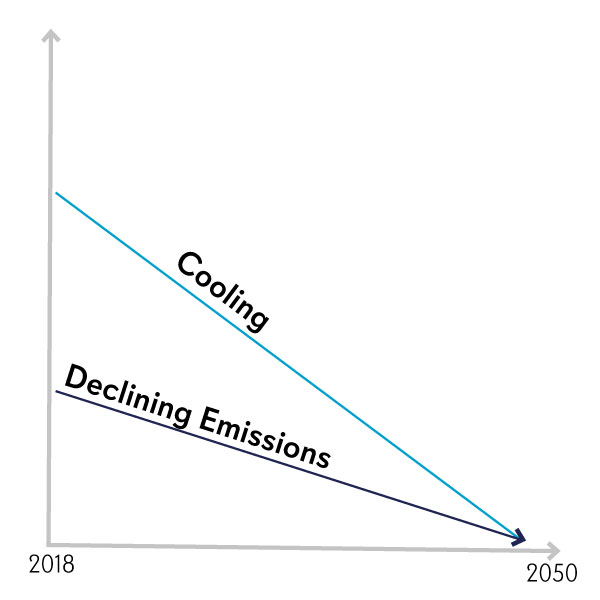
10%
immediate cooling can occur if landfill methane release is prevented, due to its short-life and high warming potential.
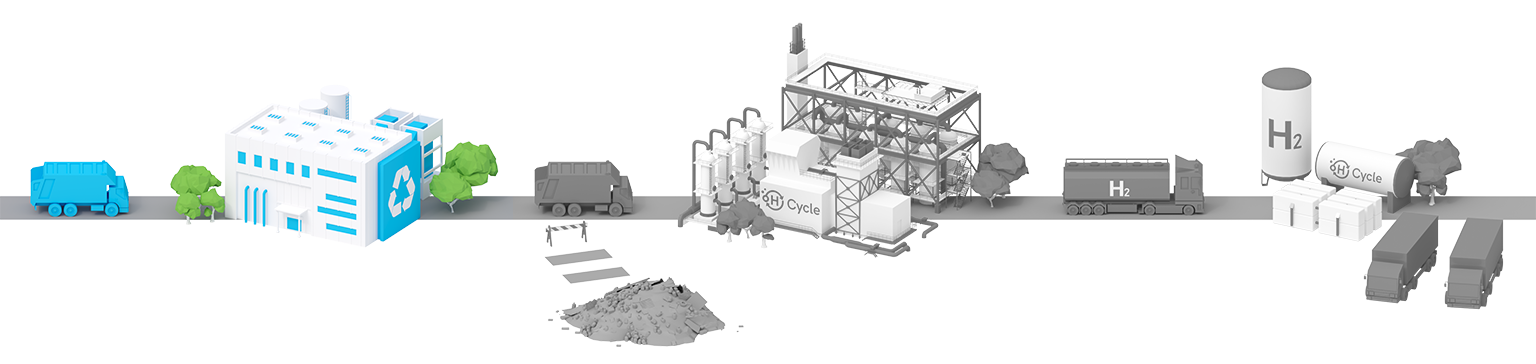
That’s where we come in
After you recycle, you H Cycle.
Recycling is still a critical part of our waste reduction. H Cycle takes the leftover waste after all recyclable material is taken out and converts it into hydrogen.
H Cycle works with heterogeneous waste mixtures, allowing us to process feedstocks typically unsuitable for composting or anaerobic digestion.
What is normally sent to a landfill for burial comes instead to H Cycle to be converted into hydrogen, resulting in a reduction of emissions.
Diverting Waste from Landfills and Incinerators
-
Addressable Market Size
In California alone, 27 million tons of waste needs to be redirected from the landfill by 2025. The processing capacity that existed in 2020 is 10 million tons, leaving 17 million tons of processing capacity needed (equivalent to 170 H Cycle facilities).
-
Organics Diversion Mandates
There is an increased scrutiny towards diversion of organics from landfills, specifically called out by the IPCC. California and Washington recently passed bills requiring 75%+ diversion of organics.
-
Improved Sustainability
Our process works with the residuals resulting from post-recycling operations and achieves further elemental recycling, converting remnant value in the waste to renewable hydrogen.
-
Unprecedented Challenges
Micro-plastics contaminating soil, water, and food; Severe landfill constraints; China’s national sword policy cracking down on western exports of recycled material; “Forever chemicals” (known as PFAS) in drinking water and food. At H Cycle, we believe that we need disruptive solutions to handle these enormous global challenges.